Artificial Intelligence (AI) encompasses the fields of science and engineering dedicated to the development of intelligent machines, particularly computer programs. It involves the use of computational systems to gain insights into human intellect, although the scope of AI extends beyond observable physiological methodologies.
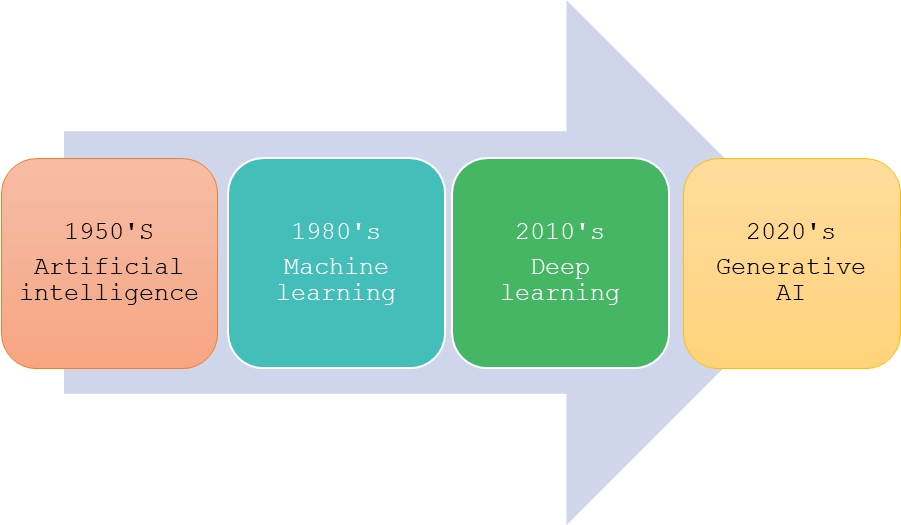
A foundational approach to understanding AI is to consider it as a series of interrelated concepts that have evolved over the past seven decades. AI enables computers and machines to replicate human capabilities such as learning, comprehension, problem-solving, decision-making, creativity, and autonomy. Beneath the umbrella of AI, machine learning is a crucial component that focuses on developing models through the training of algorithms to make predictions or determinations based on data sets. Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, employs complex multilayered neural networks, referred to as deep neural networks, to closely simulate the intricate decision-making processes of the human brain. Furthermore, generative AI, often termed “gen AI,” pertains to deep learning models that possess the ability to generate sophisticated and original content—including long-form text, high-quality images, realistic video, and audio—responsive to user prompts or requests.
Who is the father of AI?
John McCarthy is the father of artificial intelligence. He is a computer scientist who first invented the term “artificial intelligence” in 1955. McCarthy is also credited with creating Lisp, the first artificial intelligence programming language.
History
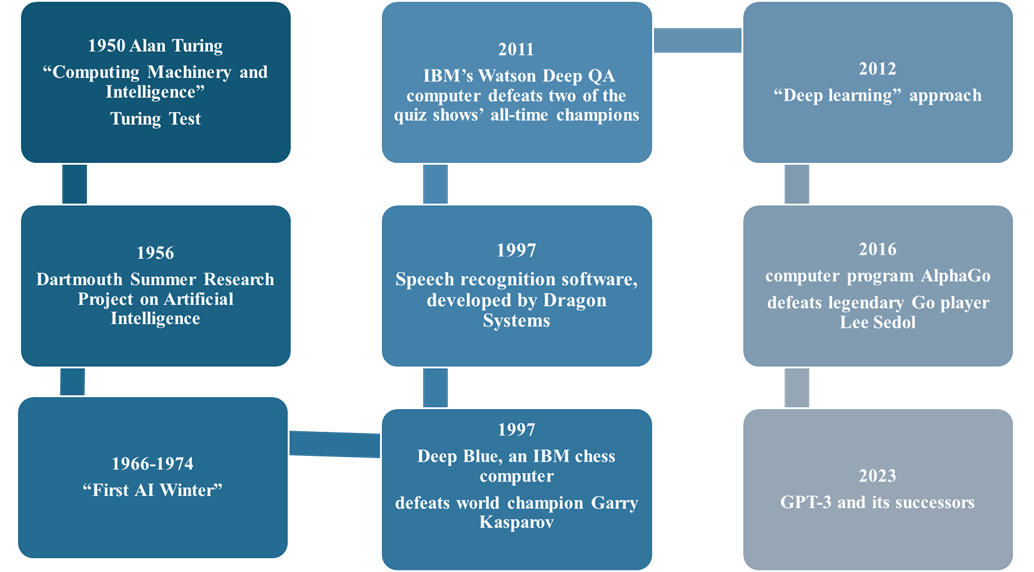
The origins of modern artificial intelligence can be traced back to Charles Babbage’s “difference engine,” the world’s first successful automatic calculator. Alan Turing, a British codebreaker who was a significant character in the Allies’ intelligence arsenal during WWII, among other accomplishments, can be viewed as a father figure for today’s incarnations of artificial intelligence. In 1950, he proposed the Turing Test, which evaluates a machine’s capacity to demonstrate intelligent behavior that is indistinguishable from that of a human.
Many consider the famous Dartmouth summer workshop in 1956 to be the starting point for serious AI research. John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon defined the AI project as “making a machine behave in ways that would be called intelligent if a human were so behaving”. In the decades that followed, definitions of AI proliferated, and Russell and Norvig (2009) compiled all of them to construct rational agents.
To cut a long story short, here are some key events and milestones in the history of artificial intelligence:
AI Facts and Figures
- Artificial Intelligence Market Growth: According to Grand View Research, the worldwide AI market is rising, worth more than $196 billion in 2024 and expected to reach $1.8 trillion by 2030.
- AI’s Economic Impact: AI has the potential to transform the global economy. According to McKinsey & Company, AI has the potential to contribute an astounding $25.6 trillion to the global economy by 2030. This economic benefit is due to AI’s capacity to automate operations, streamline processes, and create new business opportunities.
How does AI work?
While the specifics differ with AI systems, the underlying premise is data. AI systems learn and develop through exposure to massive volumes of data, detecting patterns and links that humans may overlook.
The technology uses a neural network, which relays information between layers to generate meaning from data.
Artificial intelligence training models
In broad strokes, different learning models are often used in machine learning:
- Supervised learning is a type of machine learning model that associates a specific input with an output through labeled training data (structured data). In simple terms, to train the algorithm to identify images of cats, provide it with pictures that are marked as cats.
- Unsupervised learning refers to a machine learning model that detects patterns using unlabeled data (unstructured data). The algorithm learns from the information, sorting it into groups based on different characteristics. For example, unsupervised learning excels at identifying patterns and creating descriptive models.
- Alongside supervised and unsupervised learning, a combined approach known as semi-supervised learning is frequently used, where only a portion of the data is labeled. In semi-supervised learning, there is a known outcome, but the algorithm needs to determine how to organize and structure the data to reach the desired results.
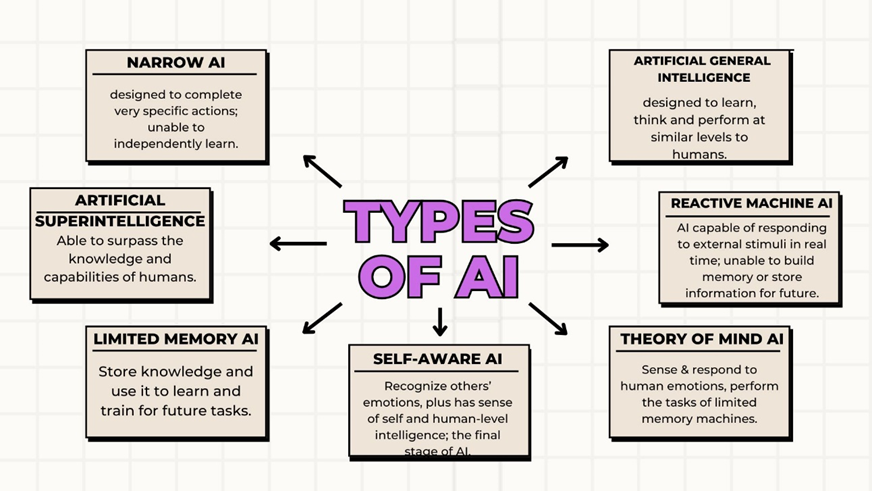
What are the different types of AI? Artificial intelligence (AI) encompasses a wide range of capabilities, each serving distinct functions and purposes.
Artificial intelligence examples
- Some of the most prevalent examples of AI currently in operation are:
- ChatGPT: Employs large language models (LLMs) to produce text in response to inquiries or comments made to it.
- Google Translate: Utilizes deep learning techniques to convert text from one language to another.
- Netflix: Implements machine learning algorithms to develop personalized recommendation systems for users based on their past viewing behavior.
- Tesla: Relies on computer vision to enable autonomous driving capabilities in their vehicles.
Strong AI vs. Weak AI
When researching artificial intelligence, you may have encountered the terms “strong” and “weak” AI. Though these terms may appear to be ambiguous, you are likely to understand what they represent.
Strong AI is defined as AI that can achieve human-level general intelligence. In other words, it simply means “artificial general intelligence.”
In contrast, weak AI refers to the limited application of widely available AI technology, such as machine learning or deep learning, to execute relatively particular tasks, such as playing chess, recommending tunes, or guiding cars. Weak AI, also known as Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), is the type of AI that is used on a daily basis.
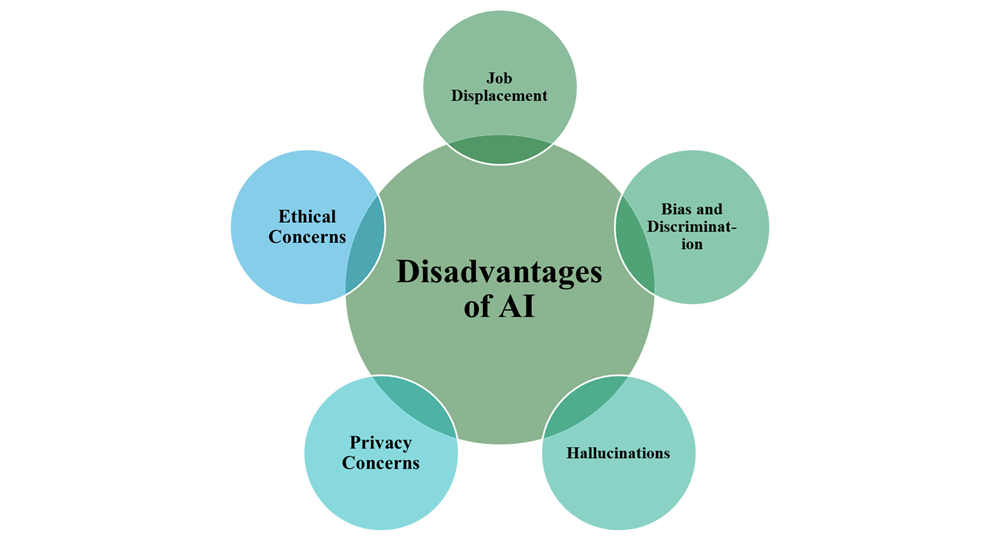
Disadvantages of AI
While artificial intelligence has its benefits, the technology also comes with risks and potential dangers to consider:
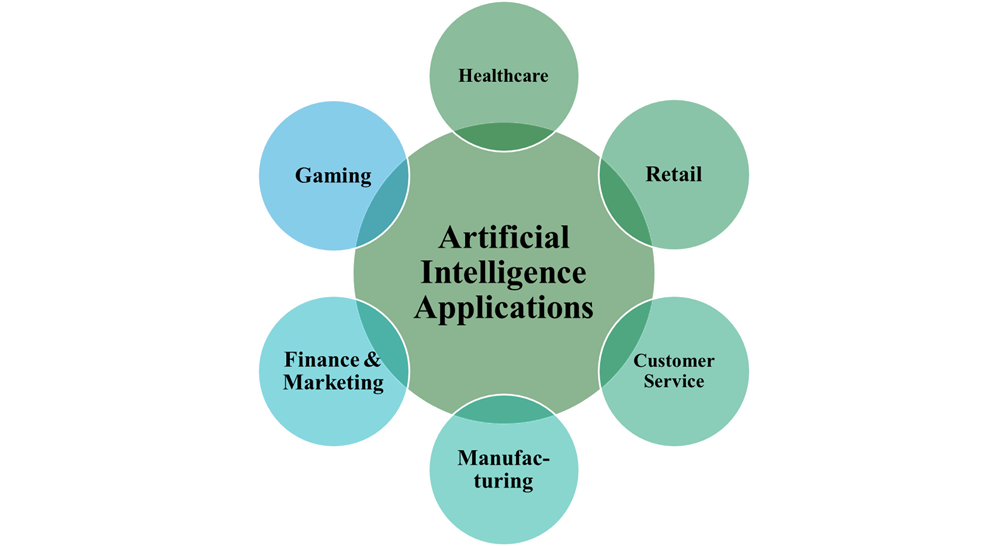
Applications of Artificial Intelligence
Future of Artificial Intelligence
The future of artificial intelligence promises to transform industries, enhance human capabilities, and solve complex challenges. It could significantly advance drug development, optimize supply chains, and inspire new art. Dario Amodei, CEO of Anthropic, suggests that AI could accelerate innovation in biological sciences by enabling more experiments and speeding up research processes. A key goal is to achieve artificial general intelligence (AGI), allowing machines to learn and function like humans, which could lead to greater automation in fields like medicine and transportation. Society is looking to federal and business-level regulations to shape the technology’s future.
References
Russell, S. J., & Norvig, P. (2016). Artificial intelligence: a modern approach. pearson.
Flasiński, M. (2016). Introduction to artificial intelligence. Springer.
Szolovits, P. (2019). Artificial intelligence and medicine. In Artificial intelligence in medicine (pp. 1-19). Routledge.
Korteling, J. H., van de Boer-Visschedijk, G. C., Blankendaal, R. A., Boonekamp, R. C., & Eikelboom, A. R. (2021). Human-versus artificial intelligence. Frontiers in artificial intelligence, 4, 622364.
Neisser, U. (2024). General, academic, and artificial intelligence. In The nature of intelligence (pp. 135-144). Routledge

MPhil, PhD Microbiology
Follow me ⬇️





Post Comment